- No products in the cart.
Institute Of
Gastroenterology
Home » The Institute of Gastroenterology, Hepatobiliary Science & Transplantation » Surgical Gastroenterology » Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric Surgery
The treatment of morbid obesity and obesity-related disorders and ailments that limit the quantity of food the stomach can contain is known as metabolic and bariatric surgery. By surgically lowering the stomach’s capacity to a few ounces, it restricts the amount of calories absorbed. Candidates for bariatric surgery have a BMI of 40 or higher, or a BMI of 35 or more with an obesity-related disease, such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease or sleep apnea. Advanced Bariatric surgery can improve or resolve more than 30 obesity-related conditions, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, sleep apnea, hypertension and high cholesterol.
Types of bariatric surgeries
Laparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric:
This is the most common bariatric surgery procedure performed all over the world. The top of the stomach is separated from the rest of the stomach. A tiny stomach of about one ounce is created. The small intestine is separated into two sections. The new, smaller stomach is subsequently attached to the small intestine’s bottom end, bypassing the portion of the tiny intestine that absorbs the most calories (the duodenum). Patients eat less and absorb fewer calories because food does not pass through the duodenum.
Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding:
A saline-filled silicone band is wrapped above the stomach section, creating a tiny pouch above the band. The rest of the stomach remains below the band. Patients have lesser food because they feel the stomach is full. After surgery, the size of the aperture can be changed by adding or removing saline from the band via a port under the skin. Patients lose 40% to 50% percent of their body weight.
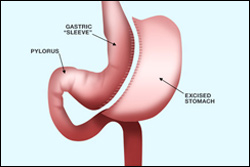
Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy:
This is a prominent process where roughly 85% of the stomach is removed leaving a sleeve-shaped stomach that resembles the shape of a banana. The new stomach is closed using surgical staples. This can be done as an open surgery or a surgery. The process remains irreversible because part of the stomach has been removed.
Biliopancreatic diversion or BPD:
A biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD/DS) gastric bypass is very comparable to sleeve gastrectomy. In this method also, part of the stomach is removed and a small tubular portion of the stomach stay behind. Additionally the first portion of the small intestine is separated just at the outlet of the stomach and the distal segment of the small intestine is combined to the newstomach.
Benefits of bariatric surgery
- Resolves 2 kind of diabetes in 73% – 83% of patients
- Cuts the hazard of growing coronary coronary heartdisease in half
- Effective remedy for obstructive sleep apnea
- Patients can increase life expectancy by 89%
- Long time effectiveness – maximumweight reduction 1-2 years after surgery and maintain a considerable weight
- Patients may lose 30% – 50%of their excess weight 6 months after surgery and 77% of theirexcess weight as early as 12 Months after surgical treatment


