Institute Of
Gastroenterology
Home » The Institute of Gastroenterology, Hepatobiliary Science & Transplantation » Surgical Gastroenterology » Surgery for Portal Hypertension
Surgery for Portal Hypertension
The portal vein system consists of the portal vein and veins that extend from the stomach, intestines, spleen, and pancreas and collaborate into portal vein. This portal vein branches into smaller tributaries to traverse the liver. Increased systemic vein resistance the system forces blood to flow through alternate channels, causing increased hepatic venous pressure which pump out. When it doesn’t flow through the liver properly, the vessels in the liver become clogged. The veins in the liver have high blood pressure, which leads to swollen veins. or varices in the esophagus, stomach, rectum, and umbilical area. These varices rupture and causes internal bleeding which can be life threatening. When the liver is obstructed, the pressure in the portal vein increases. Obstructions are divided into prehepatic, intrahepatic and post-hepatic portal hypertension.
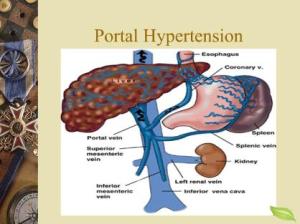
- Intrahepatic hypertension Cirrhosis and hepatic fibrosis scarring are initial intrahepatic caused due to portal hypertension. Other sicknesses that might lead to portal hypertension are fatty liver, alcohol abuse, hepatitis B and C infections, Wilson’s disease, cystic fibrosis, hemochromatosis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, biliary atresia and schistosomiasis.
- Prehepatic hypertension, the prehepatic causes are portal vein thrombosis and congenital portal vein atresia.
- Post hepatic hypertension, the post hepatic causes of portal hypertension are hepatic vein thrombosis, inferior vena cava thrombosis and restrictive pericarditis.
- Varices Blood is diverted and congregate in to another veins making way toward to heart. The veins are swollen and enlarged
- Esophageal gastric varices can be a serious condition with symptoms of hematemesis, tarry and bloody stools.
- Hepatic encephalopathy liver is incapable to shift waste products and these occur cause of lethargy.
- Ascites Due to diminish of protein in the body, will be abnormal fluid collection within the peritoneum.
- Splenomegaly Blood and blood components are trapped in the spleen causing enlargement of spleen.
- Proximal Spleno-renal shunt in a majority of Indians spleen needs to be removed because of hyprsplenism and a splenic vein end to renal vein side can be done particularly in the non-cirrhotic variety of portal hypertension.
- Distal splenorenal shunt (DSRS) This is a standard process for decompression of gastroesophageal varices. A subcostal incision is made and a fixed retractor is used to improve the intra-abdominal access.The splenic vein is identified and separated from the portal vein.It is then anastomosed to the left renal vein.
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) : Under X-ray guidance, a tubular connection is placed in the liver that connects two veins in the liver, commonly called a stent.The procedure is usually performed under general anesthesia. After making an incision in the area, first identify the internal jugular vein is first identified With the help of x-ray guidance a catheter is passed into the liver into the hepatic vein. A contrast material is then injected into the hepatic vein to plan placement of TIPS stent. Under fluoroscopy, a stent is placed connecting the portal vein into the hepatic vein. A balloon is inflated and the stent is expanded in place.
- Orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT) A bilateral subcostal incision or a J-incision is made to expose the liver. The hepatic hilum is dissected in preparation for removal of the native liver. The common area of the anastomoses is the hepatic artery and the gastroduodenal artery. The longitudinal vessels supplying the main bile duct are preserved and the portal vein is severed. Once the native liver has been removed, the transplanted liver is implanted Liver donations have their own criteria such as:
- Donor age between 18 and 60 years old
- Donor should have good health
- Donor should have a relevant blood type
- Donor should undergo multiple tests before being considered fit for the transplant.

